Understanding Tachycardia
1: The Fast-Paced Heart
- Introduction to tachycardia, a condition characterized by an abnormally rapid heart rate.
- Differentiating between normal and pathological heart rate ranges.
2: Types and Causes of Tachycardia
- Exploring various types of tachycardia, including atrial and ventricular.
- Common underlying causes, such as stress, heart disease, and medication side effects.

Causes of Tachycardia
Tachycardia can result from a multitude of factors, including
1. Stress and Anxiety: Elevated stress levels or severe anxiety can trigger episodes of tachycardia, as the body’s “fight or flight” response activates.
2. Heart Conditions: Conditions like heart disease, heart attacks, heart valve disorders, and congenital heart defects can disrupt the heart’s electrical system, leading to tachycardia.

3. Medications: Some medications, such as stimulants, decongestants, and certain asthma drugs, can increase heart rate as a side effect.
4. Anemia: A low red blood cell count can result in reduced oxygen delivery to tissues, prompting the heart to beat faster to compensate.
5. Fever: Elevated body temperature during fever can speed up heart rate.
6. High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can strain the heart, causing it to beat faster.
7. Overactive Thyroid: Hyperthyroidism can lead to excessive release of thyroid hormones, accelerating heart rate.
8. Smoking and Caffeine: Smoking and excessive caffeine consumption can stimulate the heart and lead to tachycardia.

9. Dehydration: Insufficient fluid levels can cause low blood pressure and prompt the heart to pump faster.
10. Electrolyte Imbalance: An imbalance in essential minerals like potassium, sodium, or calcium can disrupt the heart’s electrical signals.
- Symptoms of Tachycardia
Tachycardia can manifest with various symptoms, which may include
1. Rapid Heartbeat: The most common symptom, individuals with tachycardia often experience a noticeably fast heart rate.

2. Palpitations: A heightened awareness of heartbeats, which may feel like fluttering or pounding in the chest.
3. Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Insufficient blood supply to the brain due to rapid heart rate can cause dizziness or feeling faint.
4. Shortness of Breath: Inadequate blood flow can lead to difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
5. Chest Pain or Discomfort: Some individuals may experience chest pain or discomfort during tachycardia episodes.

6. Fatigue: Rapid heart rate can lead to exhaustion and fatigue, impacting daily activities.
7. Fainting (Syncope): Severe tachycardia can result in fainting spells due to decreased blood flow to the brain.
8. Anxiety: Tachycardia episodes can provoke anxiety or panic attacks.
9. Sweating: Profuse sweating may occur, especially during sudden onset tachycardia episodes.

10. Pale Skin: Insufficient circulation may cause the skin to appear pale.
Naturopathic Approaches to Tachycardia: Balancing the Heart Naturally
Tachycardia, characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate, can be managed and alleviated through various naturopathic treatments and therapies. This section explores these natural approaches to tachycardia management.
- Holistic Evaluation
1. Comprehensive Assessment: Naturopathic doctors conduct a thorough evaluation of the patient’s overall health, including lifestyle, diet, stress levels, and medical history, to identify underlying factors contributing to tachycardia.
2. Identifying Triggers: Determining specific triggers for tachycardia episodes, such as stressors or dietary habits, is a crucial step in treatment planning.
- Diet and Nutrition
1. Heart-Healthy Diet: Naturopathic practitioners emphasize the importance of a heart-healthy diet rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.

2. Nutritional Supplements: Nutritional deficiencies can contribute to tachycardia. Naturopathic doctors may recommend supplements like magnesium, potassium, and CoQ10 to support heart health.
3. Herbal Remedies: Herbs such as hawthorn, motherwort, and valerian have been traditionally used to promote cardiovascular wellness and may be incorporated into a patient’s treatment plan.

- Stress Management and Mind-Body Techniques
1. Stress Reduction: Naturopathic approaches emphasize stress management techniques, including mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and meditation, to reduce stress-induced tachycardia.
2. Yoga and Tai Chi: Mind-body practices like yoga and tai chi promote relaxation, improve circulation, and contribute to overall heart health.
- Mud Therapy
1. Mud Packs: Mud packs or poultices are applied to specific areas of the body, typically the abdomen or chest, to cool and calm the system. This can help reduce heart rate and promote relaxation.

2. Mud Baths: Immersing the body in a mud bath is a rejuvenating experience that can help alleviate stress and indirectly contribute to heart rate regulation.
- Massage Therapy
1. Swedish Massage: This gentle massage technique helps relax the body, reduce muscle tension, and alleviate stress, which can be a trigger for tachycardia.

2. Aromatherapy Massage: Using essential oils in massage can enhance relaxation and promote emotional well-being, indirectly benefiting heart rate regulation.
- Steam Therapy
1. Steam Baths: Steam baths or saunas promote detoxification, improve circulation, and induce relaxation. Regular sessions can help manage stress-related tachycardia.

2. Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam infused with calming essential oils like lavender or chamomile can have a soothing effect on the nervous system, indirectly benefiting heart rate.
- Hydrotherapy
1. Contrast Baths: Alternating hot and cold water immersion can stimulate circulation and help balance the autonomic nervous system, potentially regulating heart rate.

2. Constitutional Hydrotherapy: A naturopathic technique involving hot and cold compresses applied to the chest and back, constitutional hydrotherapy aims to promote overall wellness and balance, including heart rate regulation.
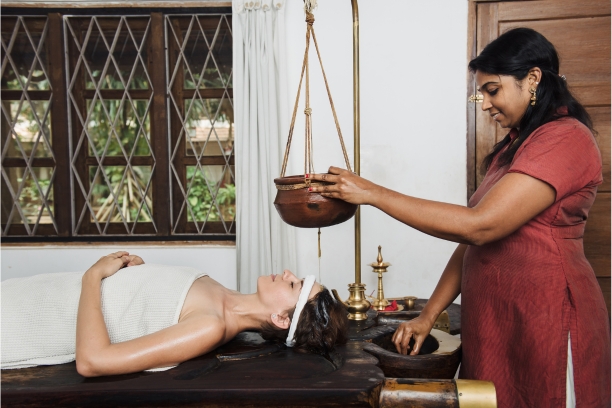
- Shirodhara Therapy
1. Shirodhara:Shirodhara therapy can help to relieve stress, promote restful sleep and calm down an agitated mind.Dilate the blood vessels and improve blood circulation, thereby enhancing brain function and beating mental fatigue and also regulates the level of serotonin in your body.

- Lifestyle Modifications
1. Smoking Cessation: Encouraging patients to quit smoking is a vital aspect of tachycardia management.
2. Caffeine and Alcohol: Reducing or eliminating caffeine and alcohol consumption can help mitigate tachycardia triggers.
3. Sleep Hygiene: Promoting healthy sleep habits to ensure adequate rest is essential for heart health.

- Integrative Care
1. Collaborative Approach: Naturopathic doctors collaborate with conventional healthcare providers to create comprehensive treatment plans for patients with tachycardia.
2. Monitoring and Adjustments: Regular follow-up appointments allow for the assessment of progress and adjustments to treatment plans as needed.
- Understanding Yogic Management
1. Holistic Wellness: Yoga is a holistic discipline that encompasses physical postures, breath control, meditation, and ethical principles. It aims to promote overall well-being and harmony in the body and mind.
2. Stress Reduction: One of the primary benefits of yoga is its ability to reduce stress, a common trigger for tachycardia. By calming the mind and reducing stress hormones, yoga can help regulate heart rate.
- Yogic Asanas for Tachycardia
1. Savasana (Corpse Pose):
- Promotes relaxation and reduces stress.
- Allows the body to rest and the heart rate to return to normal.

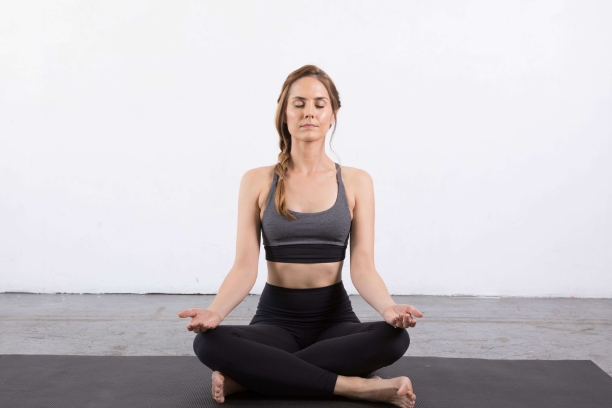
2. Sukhasana (Easy Pose):
- Encourages mindfulness and a calm, centered state.
- Supports emotional balance.

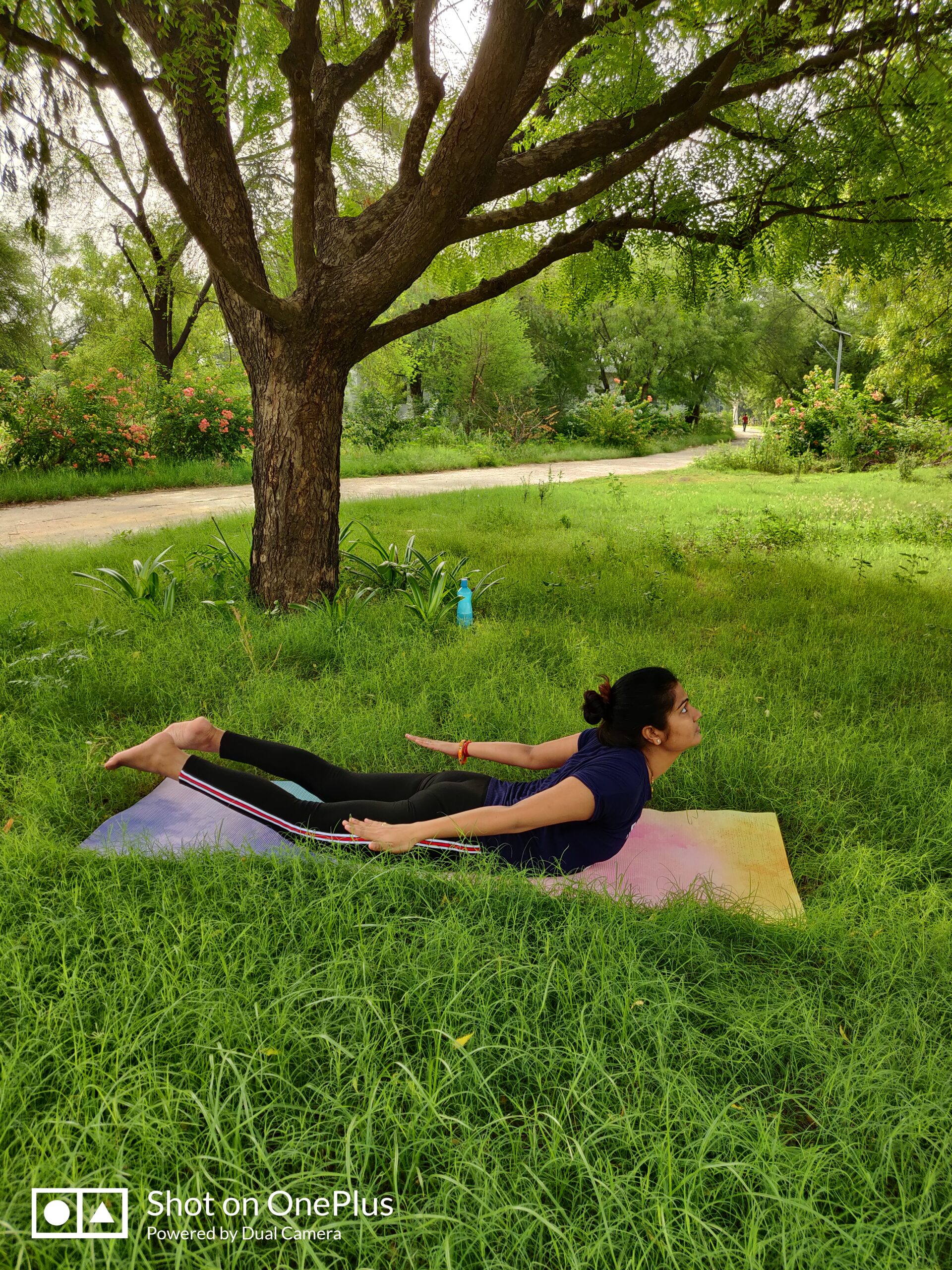
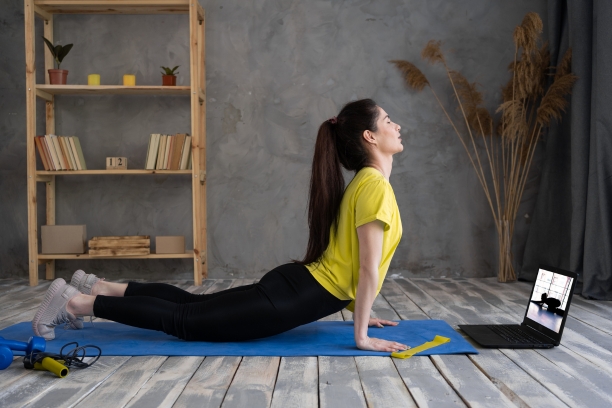
3. Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose):
- Stretches the chest and promotes better lung capacity.
- Enhances circulation and oxygenation of the heart.

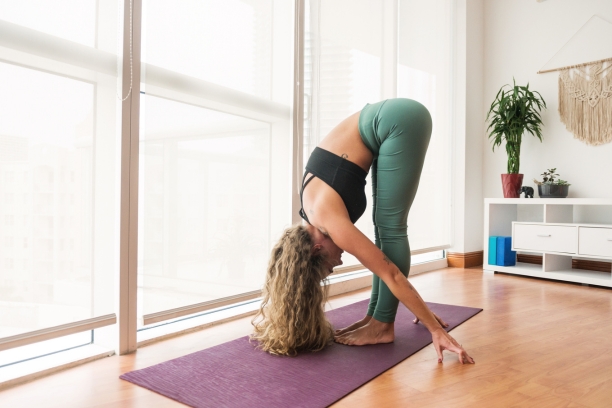
4. Uttanasana (Standing Forward Bend):
- Relieves stress and anxiety.
- Calms the nervous system.

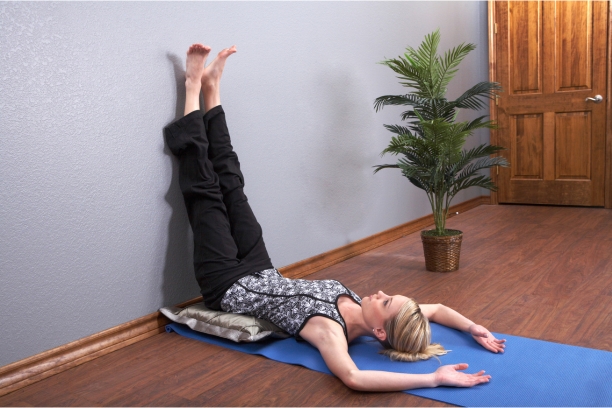
5. Viparita Karani (Legs Up the Wall Pose):
- Reduces anxiety and fatigue.
- Promotes healthy blood circulation.

6. Anulom Vilom Pranayama (Alternate Nostril Breathing):
- Balances the autonomic nervous system.
- Regulates heart rate and blood pressure.

7. Chandrabhedi Pranayama (Left Nostril Breathing):
- Technique: In this pranayama, you focus on breathing through your left nostril while keeping the right one closed. Sit comfortably and use your ring finger to close the right nostril. Inhale slowly and deeply through the left nostril, then exhale gently through the same nostril. Repeat for several breaths.
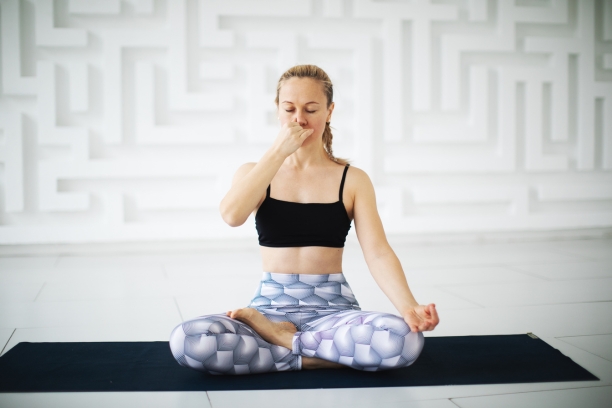

- Benefits: Chandrabhedi pranayama is known for its cooling and calming effect. It helps balance the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, potentially aiding in tachycardia management, especially if stress is a trigger.
8. Bhramari Pranayama (Humming Bee Breath):
- Technique: Sit comfortably with your eyes closed. Place your index fingers on your ears’ cartilage and take a deep breath in. As you exhale, make a humming sound similar to a bee’s buzzing. Focus on the vibration and the sound. Repeat several times.
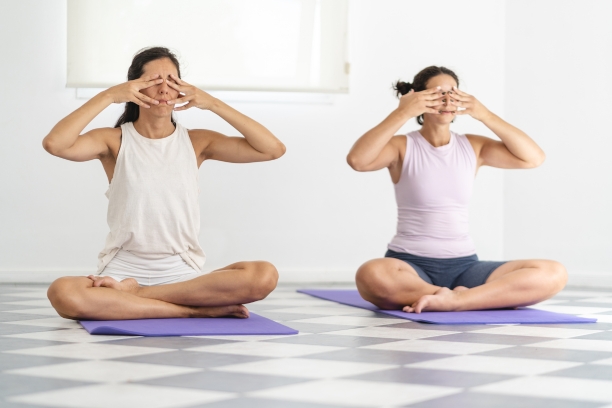

- Benefits: Bhramari pranayama is renowned for its ability to calm the mind and reduce stress and anxiety. It can be particularly helpful in managing tachycardia triggered by emotional stress.
Yogic Principles for Tachycardia Management
1. Breath Awareness: Yoga teaches breath awareness, which can help individuals notice and control rapid or shallow breathing associated with tachycardia.
2. Mindfulness Meditation: Regular meditation practice cultivates a calm mind and reduces stress, indirectly benefiting heart rate regulation.

3. Lifestyle Harmony: Yoga encourages a balanced lifestyle that includes proper nutrition, regular exercise, and adequate rest—all essential components of tachycardia management.
4. Ethical Living: Practicing ethical principles, such as non-violence (ahimsa) and truthfulness (satya), can contribute to emotional well-being and heart health.
Conclusion:
- Encouraging individuals with tachycardia to explore naturopathic and holistic approaches alongside conventional treatments.
- Naturopathic approaches to tachycardia offer a holistic and individualized path to heart health.
- Yoga offers a holistic approach to managing tachycardia by addressing both physical and emotional aspects.
- The practice of specific yogic asanas and pranayama techniques can help regulate heart rate and reduce stress, promoting heart health and overall well-being.