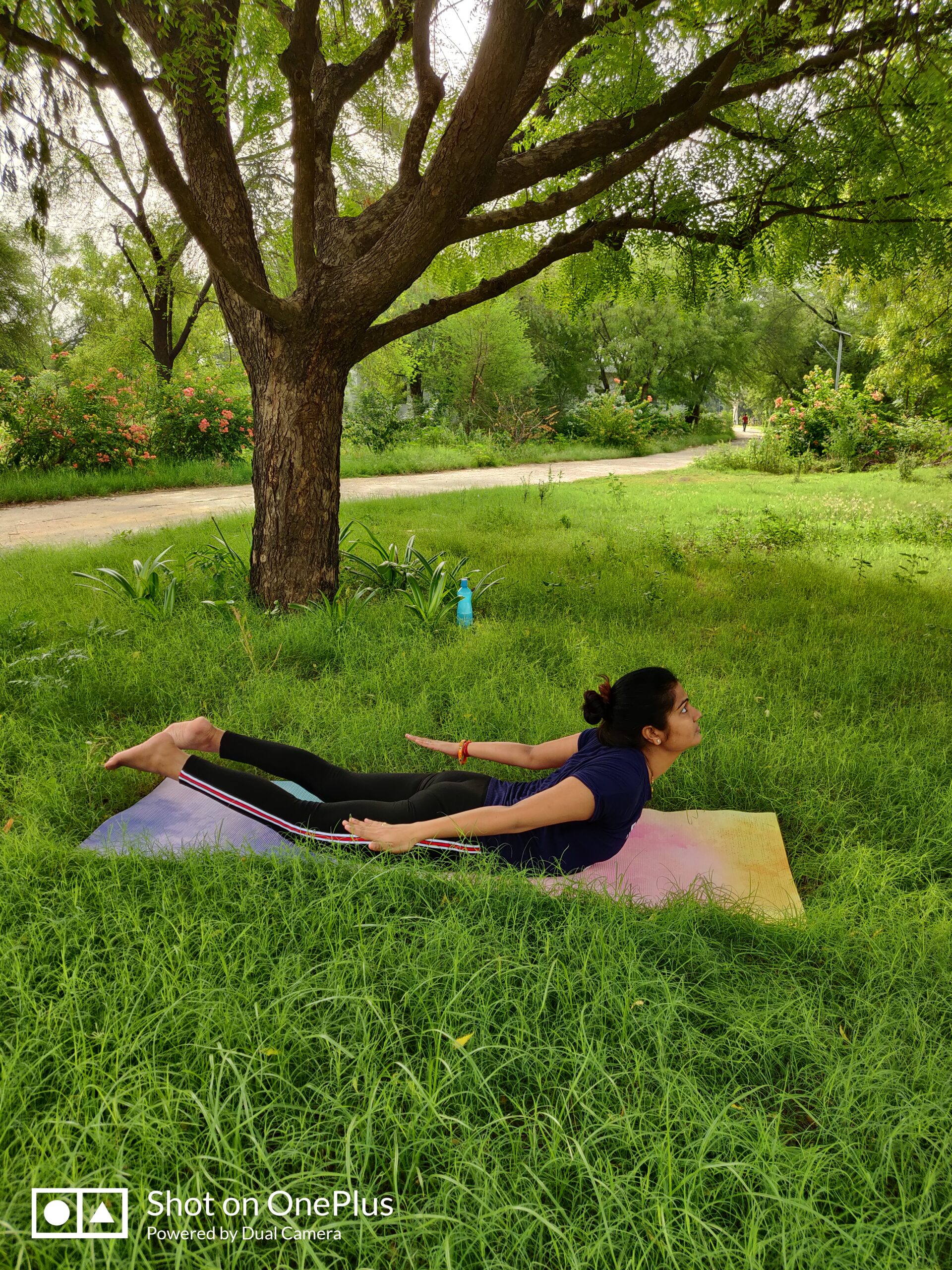
Paralysis attacks, often resulting from strokes or neurological disorders, can be life-altering. This article explores naturopathic management, treatments, and therapies that offer a holistic and complementary approach to paralysis recovery. From lifestyle modifications to herbal remedies and physical therapies, we delve into a comprehensive strategy to enhance the quality of life for those affected by paralysis.
The Impact of Paralysis Attacks
- Understanding Paralysis: Paralysis is the loss of muscle function in part of the body, typically caused by damage to the nervous system. It can profoundly affect mobility and daily life.

Causes and Symptoms of Paralysis Attacks
Understanding the root causes and recognizing the symptoms of paralysis attacks is crucial for effective management and early intervention. In this chapter, we delve into the various factors that can lead to paralysis and the signs that individuals and caregivers should be aware of.
1. Ischemic Stroke as a Primary Cause
- A Closer Look at Ischemic Stroke: Ischemic strokes are a leading cause of paralysis attacks. Explore how blood clots and blocked arteries can result in this type of stroke.
- Risk Factors: Understand the risk factors that increase the likelihood of ischemic strokes, including hypertension, diabetes, and lifestyle choices.
- Prevention Strategies: Highlight the importance of stroke prevention through lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise.
2. Hemorrhagic Strokes: Another Culprit
- Understanding Hemorrhagic Strokes: Hemorrhagic strokes, caused by bleeding in the brain, can also lead to paralysis. Explain how an aneurysm or blood vessel rupture can trigger this type of stroke.
- Risk Factors: Discuss the risk factors for hemorrhagic strokes, including genetics and underlying medical conditions.
- Preventive Measures: Explore strategies to prevent hemorrhagic strokes, including blood pressure management and avoidance of certain medications.
3. Neurological Disorders and Paralysis
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Examine how autoimmune conditions like MS can result in paralysis and discuss the importance of early diagnosis and management.
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): Provide insights into the progression of ALS and the challenges individuals face in coping with paralysis.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS): Discuss GBS as a temporary but severe neurological disorder that can cause muscle weakness and paralysis.
4. Traumatic Causes of Paralysis
- Spinal Cord Injuries: Explain how traumatic incidents such as car accidents or falls can damage the spinal cord, leading to paralysis.
- Head Injuries: Discuss the impact of traumatic brain injuries on motor function and paralysis risk.
- Preventive Measures: Offer safety tips and preventive measures to reduce the risk of traumatic paralysis.
5. Recognizing Symptoms of Paralysis
- Sudden Weakness or Numbness: Highlight the importance of recognizing early warning signs such as sudden weakness or numbness in specific body parts.
- Loss of Coordination: Explain how a loss of coordination and difficulty in walking or moving can indicate paralysis.
- Speech and Vision Changes: Discuss how speech difficulties and vision changes can accompany certain types of paralysis attacks.
6. Beyond Physical Symptoms
- Emotional Impact: Explore the emotional toll that paralysis can have on individuals and their loved ones.
- Cognitive Challenges: Discuss potential cognitive challenges that can arise alongside physical symptoms.
Naturopathic Treatments and Therapies for Paralysis Management
1. Herbal Remedies for Nervous System Support
- Gingko Biloba: Highlight the potential benefits of gingko biloba in enhancing blood circulation and supporting nerve function.
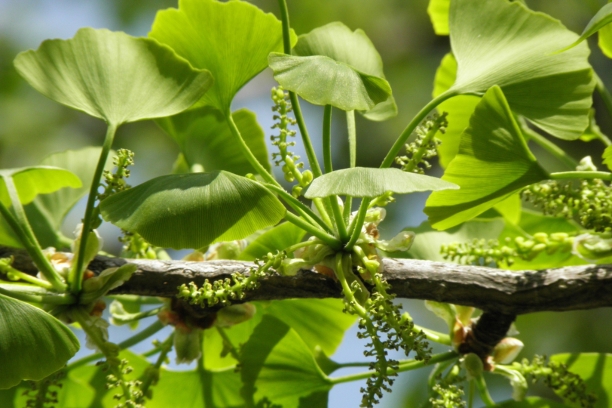

- Ashwagandha: Discuss how this adaptogenic herb can help reduce stress, promote nerve regeneration, and improve muscle strength.
- Gotu Kola: Explore how gotu kola can aid in tissue healing and potentially contribute to paralysis recovery.
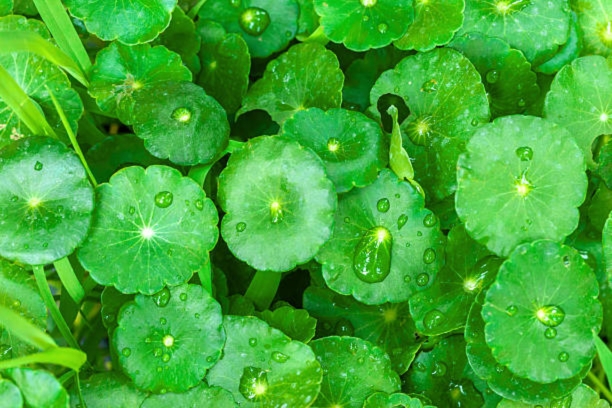

2. Dietary Modifications for Neurological Health
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Explain the importance of an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids in reducing inflammation in the nervous system.
- Vitamin and Mineral Supplementation: Discuss the role of vitamins like B-complex and minerals like magnesium in supporting nerve health.
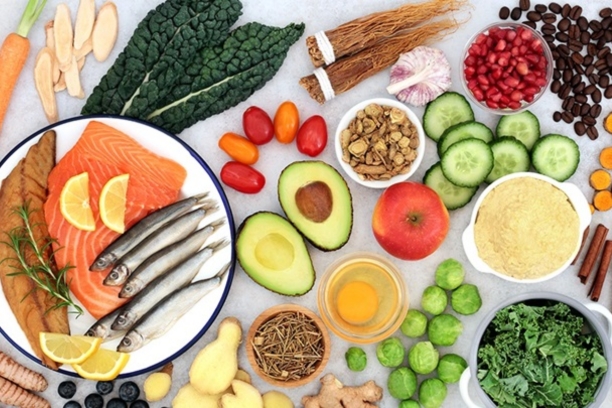

- Hydration and Electrolyte Balance: Emphasize the significance of proper hydration and maintaining electrolyte balance for nerve function.
3. Hydrotherapy: Harnessing the Healing Power of Water
- Contrast Baths: Explore how alternating hot and cold water immersions can stimulate circulation and promote muscle recovery.
- Steam Baths: Discuss how steam baths can aid in relaxation and indirectly contribute to improved muscle function.
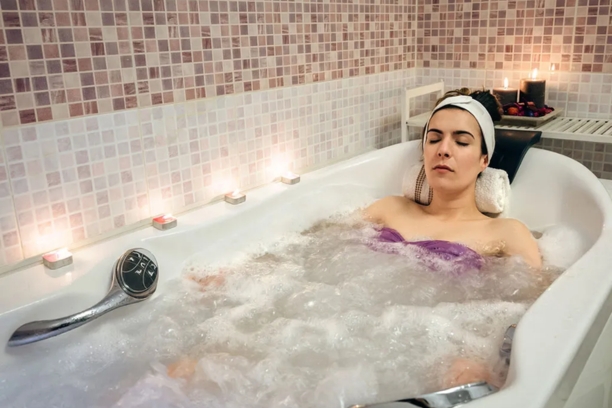

- Hydrotherapy Techniques: Describe various hydrotherapy techniques that individuals can incorporate into their routine.
4. Massage Therapy
Massage therapy is a hands-on approach that can provide numerous benefits for those on the path to paralysis recovery.
- Introduction to Massage Therapy: Explain the principles and techniques of massage therapy, highlighting its role in improving blood circulation, muscle relaxation, and stress reduction.
- Benefits for Paralysis Recovery: Discuss how massage therapy can alleviate muscle stiffness, reduce pain, and promote a sense of relaxation, which is crucial for individuals with limited mobility.
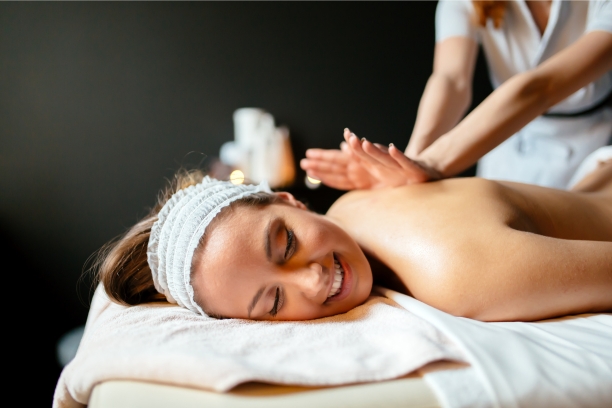

- Different Modalities: Explore various massage modalities, such as Swedish massage, deep tissue massage, and myofascial release, and how they can be tailored to individual needs.
- Professional Guidance: Emphasize the importance of seeking massage therapy from licensed professionals experienced in working with clients in paralysis recovery.
2. Shirodhara Therapy
Shirodhara is a traditional Ayurvedic therapy that involves a continuous flow of warm oil or other liquids onto the forehead. It offers profound relaxation and therapeutic benefits.
- Introduction to Shirodhara: Explain the origins and principles of Shirodhara therapy, emphasizing its calming and rejuvenating effects on the nervous system.
- Benefits for Paralysis Recovery: Discuss how Shirodhara can alleviate stress, anxiety, and sleep disturbances often associated with paralysis, promoting mental and emotional well-being.
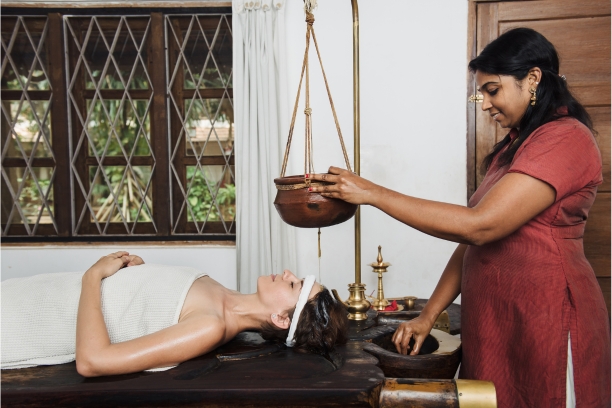

- Procedure: Describe the Shirodhara procedure, including the use of specific oils and the gentle pouring of liquid onto the forehead.
- Professional Ayurvedic Practitioners: Encourage individuals to seek Shirodhara therapy from qualified Ayurvedic practitioners who can tailor the treatment to their unique needs.
4. The Role of Physical Therapies
- Physiotherapy: Explain how physiotherapy can help individuals regain muscle strength, mobility, and independence.
- Occupational Therapy: Discuss strategies for adapting daily activities to accommodate physical limitations.
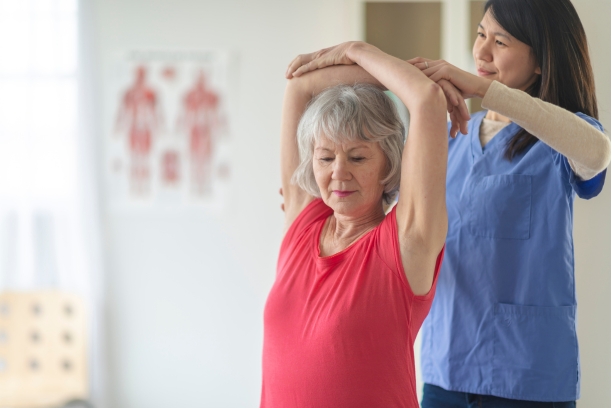

- Speech Therapy: Address communication challenges that can accompany paralysis and the role of speech therapy in improving speech and swallowing.
5. Mind-Body Connection: Stress Reduction and Visualization
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Explore mindfulness practices and relaxation exercises that can help manage stress, which can hinder recovery.
- Visualization and Affirmation: Discuss the power of the mind in enhancing healing and motivation.
6. Complementary Therapies
- Acupuncture: Examine the potential of acupuncture in stimulating nerve regeneration and enhancing overall well-being.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: Highlight the benefits of these practices in improving balance, flexibility, and emotional well-being.
- Aromatherapy: Describe how essential oils can be used to enhance mood and relaxation during the recovery process.
Yogic Management for Paralysis Recovery
Yoga, with its emphasis on physical postures, breath control, and meditation, offers a unique and powerful approach to paralysis management. In this chapter, we explore various yogasanas (yoga postures) and yogic management techniques that can aid in rehabilitation, improve muscle strength, and enhance overall well-being for individuals recovering from paralysis.
1. Understanding Yogic Management
- Yoga as a Holistic Practice: Discuss how yoga addresses physical, mental, and emotional aspects of well-being.
- Benefits for Paralysis Recovery: Highlight the potential benefits of yoga, such as improved flexibility, muscle tone, and stress reduction.
2. Gentle Yogasanas for Beginners
1. Tadasana (Mountain Pose)
Tadasana, often referred to as the Mountain Pose, serves as a fundamental posture in yoga, offering numerous benefits for those on the path to paralysis recovery.
- Pose Description: Explain the correct alignment and posture of Tadasana, emphasizing standing tall with feet together, arms relaxed, and shoulders down.
- Benefits for Paralysis Recovery: Discuss how Tadasana can improve posture, balance, and body awareness, which are essential for rehabilitation.
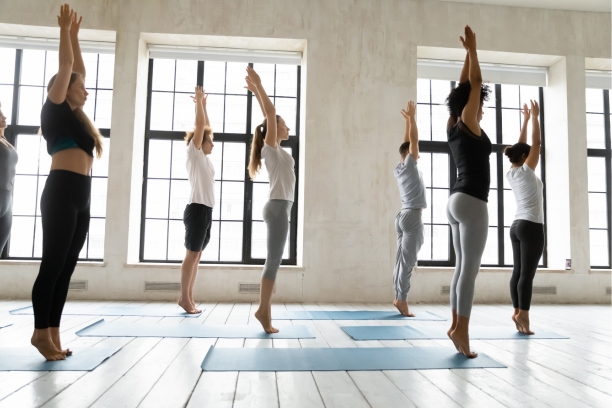

- Breathing Awareness: Highlight the importance of mindful breathing while holding the pose to enhance relaxation and concentration.
- Modifications: Provide variations and props that individuals with different levels of mobility can use to practice Tadasana safely.
2. Vrikshasana (Tree Pose)
Vrikshasana, known as the Tree Pose, focuses on balance and concentration, making it an excellent choice for individuals seeking to improve stability during paralysis recovery.
- Pose Description: Explain the steps to perform Vrikshasana, including shifting weight onto one leg, placing the opposite foot on the inner thigh or calf, and balancing with arms overhead.
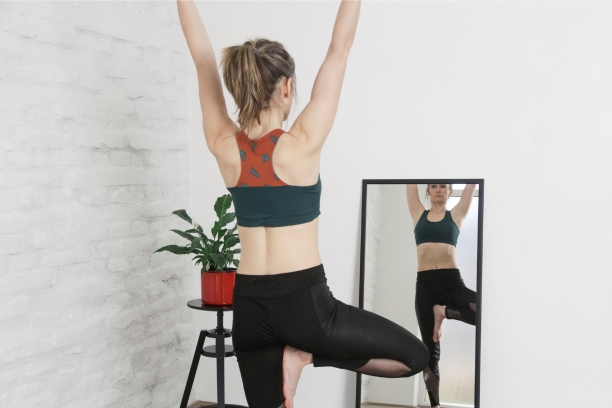

- Benefits for Paralysis Recovery: Discuss how Vrikshasana can enhance leg strength, stability, and mental focus, assisting with mobility and coordination.
- Cautions and Modifications: Offer guidance on adapting the pose for those who may require support or have limitations in leg mobility.
3. Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose)
Bhujangasana, or the Cobra Pose, is a gentle backbend that can aid in spinal flexibility and provide relief from back discomfort, making it suitable for individuals in paralysis recovery.
- Pose Description: Explain the steps to perform Bhujangasana, including lying face down, placing hands under the shoulders, and lifting the chest while keeping the pelvis grounded.
- Benefits for Paralysis Recovery: Discuss how Bhujangasana can help improve spinal mobility, strengthen the back muscles, and enhance overall posture.

- Breathing Technique: Highlight the synchronization of breath with the gentle arching of the spine, promoting relaxation and openness in the chest.
- Adaptations: Provide options for adapting the pose based on individual abilities and comfort levels.
3. Intermediate Yogasanas for Progression
Salabhasana (Locust Pose)
Salabhasana, commonly known as the Locust Pose, is an intermediate backbend that offers multiple benefits for individuals on the path to paralysis recovery.
- Pose Description: Explain how to perform Salabhasana, emphasizing the importance of lying face down, lifting the legs and upper body, and engaging the back muscles.
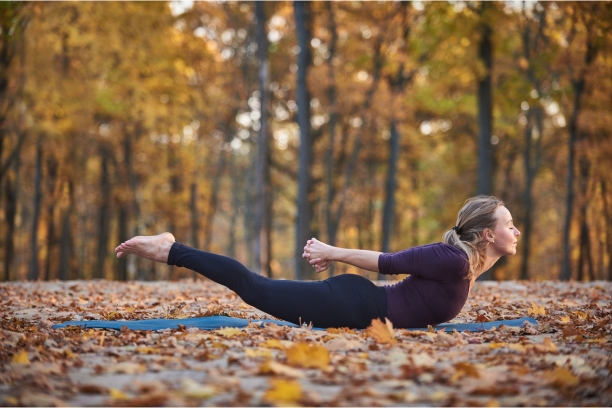

- Benefits for Paralysis Recovery: Discuss how Salabhasana can help strengthen the lower back, buttocks, and leg muscles, which are essential for improved mobility.
- Cautions and Modifications: Highlight precautions and variations of the pose for individuals with different levels of mobility and flexibility.
2. Ustrasana (Camel Pose)
Ustrasana, or the Camel Pose, is a deep backbend that offers benefits for spinal flexibility and emotional well-being.
- Pose Description: Explain the steps to perform Ustrasana, including kneeling, arching the back, and reaching for the heels.
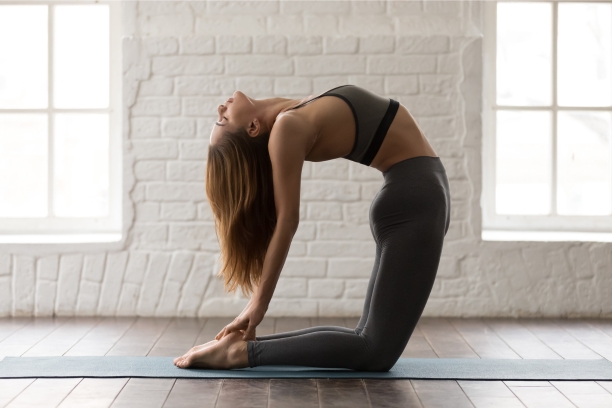

- Benefits for Paralysis Recovery: Discuss how Ustrasana can help improve posture, relieve back pain, and open the chest, enhancing lung capacity.
- Cautions and Modifications: Provide guidance on how to adapt the pose for individuals with limited mobility or flexibility.
3. Virabhadrasana II (Warrior II)
Virabhadrasana II, often called Warrior II, is a powerful standing pose that engages the legs, hips, and core muscles, making it beneficial for paralysis recovery.
- Pose Description: Explain the alignment and positioning of Virabhadrasana II, emphasizing the strength and stability required.
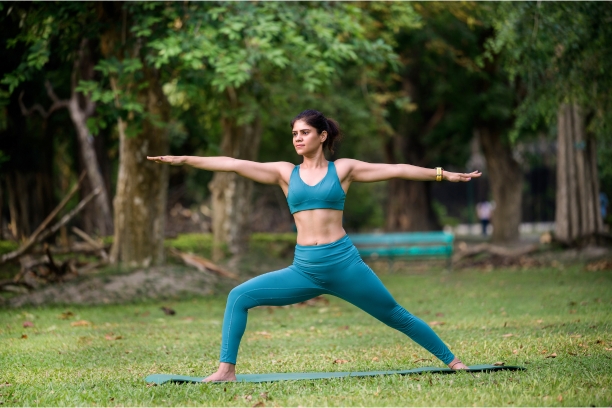

- Benefits for Paralysis Recovery: Discuss how this pose can enhance leg strength, balance, and mental focus, which are crucial for mobility and rehabilitation.
- Cautions and Modifications: Provide guidance on adjusting the pose to accommodate individual abilities and needs.
4. Advanced Yogasanas for Muscle Recovery
1. Ardha Chandrasana (Half Moon Pose)
Ardha Chandrasana, also known as the Half Moon Pose, is a challenging balance posture that offers numerous benefits for individuals seeking to regain strength and balance during paralysis recovery.
- Pose Description: Explain the steps to perform Ardha Chandrasana, focusing on balancing on one leg while extending the other leg and arm towards the sky.\
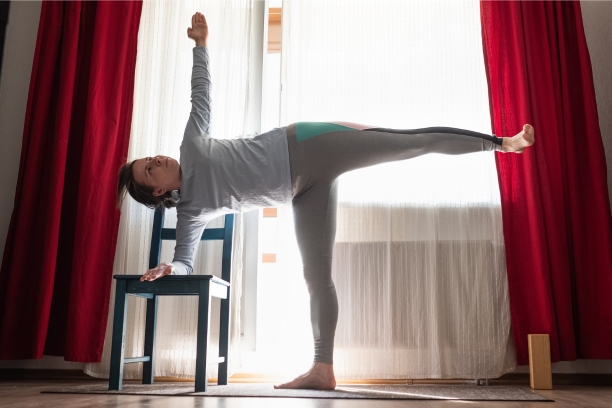

- Benefits for Paralysis Recovery: Discuss how Ardha Chandrasana can improve balance, strengthen leg muscles, and enhance concentration, supporting mobility and coordination.
- Cautions and Modifications: Offer guidance on adapting the pose for individuals who may require support or have limited mobility.
2. Setu Bandhasana (Bridge Pose)
Setu Bandhasana, or the Bridge Pose, is an excellent asana for individuals in paralysis recovery, as it helps in strengthening the back muscles, improving spinal flexibility, and enhancing overall posture.
- Pose Description: Explain how to perform Setu Bandhasana, including lying on the back, bending the knees, and lifting the hips while keeping the feet and palms grounded.
- Benefits for Paralysis Recovery: Discuss how Setu Bandhasana can support the rehabilitation process by engaging various muscle groups, especially the back and legs.
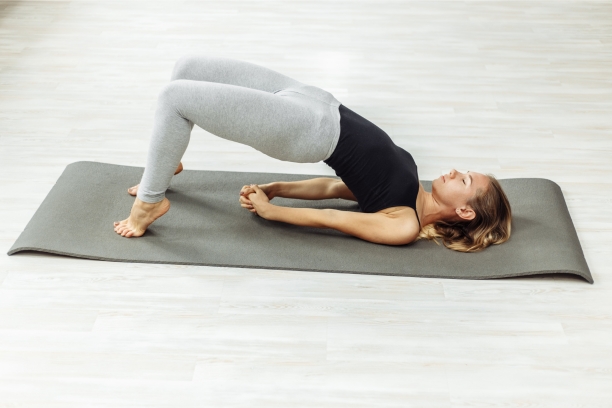

- Breathing Technique: Highlight the coordination of breath with the lifting and lowering of the hips for relaxation and focus.
- Adaptations: Provide options for modifying the pose based on individual needs and abilities.
3. Dhanurasana (Bow Pose)
Dhanurasana, often referred to as the Bow Pose, is an intermediate backbend that can be particularly beneficial for individuals working on improving their spinal flexibility and muscle tone during paralysis recovery.
- Pose Description: Explain the steps to perform Dhanurasana, including lying on the stomach, bending the knees, and reaching back to hold the ankles while lifting the chest and thighs.
- Benefits for Paralysis Recovery: Discuss how Dhanurasana can enhance back strength, stimulate the abdominal organs, and promote flexibility in the spine.
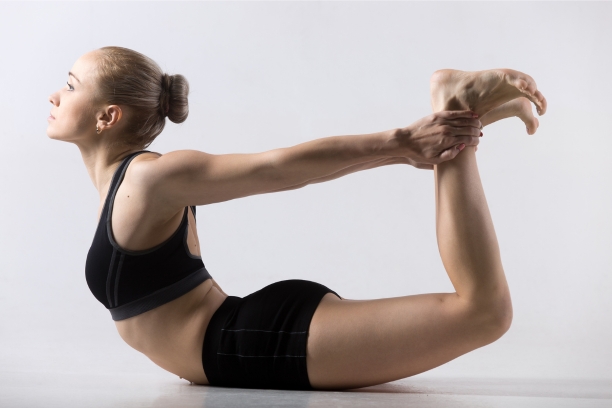

- Breathing Awareness: Emphasize the importance of synchronized breath with the movement, facilitating relaxation and expansion in the chest.
- Modifications: Offer variations and props to accommodate different levels of mobility and comfort.
5. Pranayama Techniques for Energy and Relaxation
- Anulom Vilom Pranayama: Explain the alternate nostril breathing technique and its potential to balance the nervous system.

- Surya Bhedi Pranayama: Discuss the energizing effect of right nostril breathing and its potential for improving vitality.
- Kapalbhati Pranayama: Explore the benefits of this cleansing breath for mental clarity and improved lung function.
- Bhastrika Pranayama: Describe the rapid breath technique and its potential to boost energy levels.
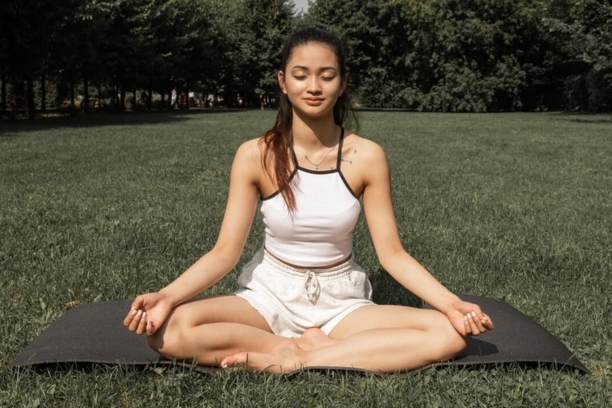

6. The Role of Meditation and Mindfulness
- Dhyana (Meditation): Discuss meditation as a practice to calm the mind, reduce stress, and enhance mental focus.
- Mindfulness Techniques: Explore mindfulness exercises and their potential to improve emotional well-being and resilience.
7. Personalized Yogic Management Plans
- Creating Individualized Yoga Sequences: Explain the importance of tailoring yoga practices to individual abilities and needs.
- Yoga Therapy: Discuss the role of yoga therapists in guiding individuals through safe and effective practices.
Conclusion:
- The significance of embracing a holistic approach in paralysis management.
- Empowering individuals to take charge of their recovery and regain a fulfilling life.
- Emphasize the importance of awareness and early intervention in managing paralysis attacks.
- Emphasize the significance of a holistic approach in paralysis management, addressing physical, emotional, and lifestyle factors.
- Emphasize the transformative potential of yoga in paralysis management, from physical rehabilitation to mental and emotional well-being.
- Encourage individuals to explore yoga as a complementary therapy on their path to recovery, under the guidance of