Introduction
Hyperthermia and hypothermia are two opposite temperature-related conditions that can have severe health consequences if not managed promptly. Hyperthermia occurs when the body overheats, while hypothermia occurs when the body loses heat faster than it can produce it. This comprehensive guide explores the naturopathic approaches to managing hyperthermia and hypothermia, offering unique and holistic solutions for these conditions.

Table of Contents
- Hyperthermia: Unraveling the Heat-Related Dilemma
- What Is Hyperthermia?
- Causes of Hyperthermia
- Symptoms of Hyperthermia
- Conventional vs. Naturopathic Management
- Naturopathic Therapies for Hyperthermia
- Hydration and Cooling Foods
- Herbal Remedies for Heat Relief
- Hydrotherapy and Cooling Baths
- Yogic Practices for Cooling the Body
- Mind-Body Techniques for Heat Stress

- Hypothermia: Understanding the Chilling Effect
- What Is Hypothermia?
- Causes of Hypothermia
- Stages of Hypothermia
- Conventional vs. Naturopathic Management
- Naturopathic Approaches for Hypothermia
- Warming Foods and Nutritional Support
- Herbal Remedies for Warming the Body
- Hydrotherapy and Heat-Inducing Baths
- Yogic Practices for Body Warmth
- Mind-Body Techniques to Regulate Body Temperature

- Preventive Strategies for Hyperthermia and Hypothermia
- Staying Safe in Extreme Temperatures
- Nutrition and Lifestyle Practices
- Yoga and Meditation for Temperature Regulation
- Herbal Supplements for Thermal Balance
Causes of Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia can arise from various causes, including environmental factors, physical exertion, and underlying medical conditions. Understanding these causes is essential for effective prevention and management.
Environmental Factors:
- Hot Weather: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures and humidity can overwhelm the body’s ability to cool itself, leading to hyperthermia.
- Heat Waves: During heatwaves, the risk of hyperthermia significantly increases, especially in vulnerable populations.
- Dehydration: Inadequate fluid intake reduces the body’s ability to sweat and cool down, making dehydration a common cause of hyperthermia.

Physical Exertion:
- Strenuous Activity: Engaging in vigorous physical activity in hot conditions can generate excessive body heat.
- Overexertion: Pushing the body beyond its limits can lead to heat-related illnesses.
Underlying Medical Conditions:
- Heat-Related Disorders: Certain medical conditions, such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes, can impair the body’s ability to regulate temperature.
- Medications: Some medications affect the body’s response to heat, increasing the risk of hyperthermia.
Causes of Hypothermia
- Exposure to Cold Weather: Prolonged exposure to cold temperatures, especially without adequate protection, is a primary cause of hypothermia.
- Wet Clothing: Wet clothes can significantly increase heat loss from the body.
- Wind Chill: Wind can strip away body heat, making you more susceptible to hypothermia.

- Submersion in Cold Water: Falling into cold water or staying in it for extended periods can lead to rapid heat loss.
- Inadequate Clothing: Insufficient or inappropriate clothing for the weather conditions can increase the risk.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, medications, and age-related factors can affect the body’s ability to regulate temperature.
Symptoms of Hyperthermia
Recognizing the symptoms of hyperthermia is crucial for timely intervention. Symptoms can range from mild heat exhaustion to severe heat stroke. Common signs of hyperthermia include:

- Muscle cramps
- Heavy sweating
- Rapid heartbeat
- Nausea or vomiting
- Weakness and fatigue
- Headache
- Dizziness or fainting
- **Confusion or altered mental state
- High body temperature
- Skin that may be hot, dry, or moist
- **Shallow breathing
Symptoms of Hypothermia
- Shivering: Shivering is the body’s natural response to cold and an early sign of hypothermia.
- Cold, Pale Skin: The skin may appear cold and pale as blood vessels constrict to conserve heat.
- Confusion: Hypothermia can cause confusion, slurred speech, and impaired judgment.

- Weakness and Fatigue: Muscle weakness and extreme fatigue are common symptoms.
- Slow Breathing and Heart Rate: Breathing and heart rate may become slow and irregular.
- Loss of Coordination: Fine motor skills and coordination may deteriorate.
- Severe Hypothermia: In severe cases, symptoms can progress to unconsciousness, dilated pupils, and cardiac arrest.
Naturopathic Treatments and Therapies for Hyperthermia
Naturopathic treatments for hyperthermia focus on restoring balance to the body and promoting natural healing processes. These therapies complement conventional treatments and can aid in prevention.
Herbal Remedies
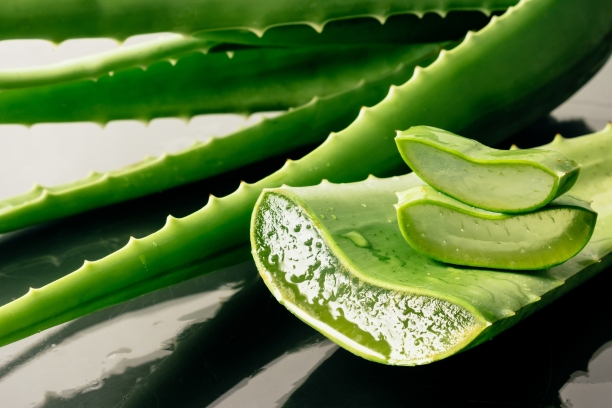
1. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is well-known for its cooling properties. Applying aloe vera gel to the skin can help reduce the heat and soothe burns or rashes caused by hyperthermia.

2. Peppermint
Peppermint contains menthol, which provides a cooling sensation. Drinking peppermint tea or applying peppermint oil to the skin can help alleviate heat-related discomfort.

Nutritional Therapy
1. Hydration
Proper hydration is crucial in managing hyperthermia. Drinking water and consuming hydrating foods like watermelon, cucumber, and leafy greens can help maintain adequate fluid balance.

2. Electrolytes
Loss of electrolytes through sweating can lead to imbalances. Consuming foods rich in potassium, sodium, and magnesium, such as bananas, coconut water, and nuts, can help restore these essential minerals.

Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy uses water in various forms to promote healing. In cases of hyperthermia, cool baths or compresses can be effective. Immerse the body in a cool (not cold) bath or use damp, cool towels to lower body temperature.

Detoxification
Hyperthermia often involves the accumulation of toxins due to heat-related stress. Detoxification can help the body eliminate these toxins, reducing the risk of complications. Methods like hydrotherapy, sauna therapy, and dietary adjustments play a significant role in detoxification.

Mind-Body Practices
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate hyperthermia symptoms. Mind-body practices like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga promote relaxation and mental clarity. They help manage stress and improve overall well-being.

Physical Therapy
Exercises aimed at improving circulation and cardiovascular health can be beneficial. Low-intensity activities like walking and gentle yoga can help the body recover from hyperthermia.

Acupuncture and Acupressure
These therapies can help balance the body’s energy and alleviate discomfort associated with hyperthermia.
Herbal Teas
Consuming herbal teas like chamomile, lavender, or hibiscus can have a calming and cooling effect. These teas promote relaxation and aid in body temperature regulation.

Naturopathy Management of Hypothermia
Naturopathic approaches can complement conventional treatments for hypothermia, focusing on natural methods to help raise body temperature and promote overall well-being. Here are some naturopathy strategies for managing hypothermia:
1. Herbal Remedies:
- Herbal teas and infusions containing warming herbs like ginger, cinnamon, and cayenne pepper can help raise body temperature.

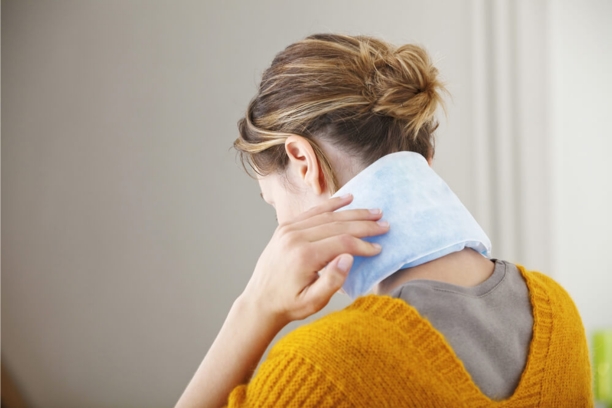
2. Warm Compresses:
- Applying warm compresses to the body’s core areas, such as the neck, chest, and groin, can help gradually increase body temperature.

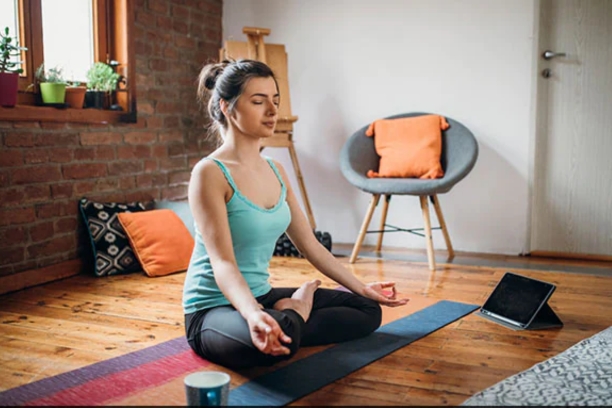
3. Pranayama and Yoga:
- Yogic practices like Bhastrika Pranayama (Bellows Breath) generate internal heat and stimulate circulation.
- Asanas that focus on core strength and twisting movements can help warm the body from within.
4. Hydrotherapy:
- Hydrotherapy techniques, such as warm baths, can assist in gently raising the body’s temperature.
5. Meditation and Deep Breathing:
- Meditation can calm the mind and reduce stress, which may help the body recover more efficiently.
- Deep breathing exercises can increase oxygen intake and support vital organ functions.

6. Nutrition and Hydration:
- Eating warm, nourishing foods can provide the body with energy to generate heat.
- Proper hydration is essential to maintain bodily functions.

7. Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Dressing in warm, layered clothing is crucial for preventing hypothermia.
- Avoiding prolonged exposure to cold weather and staying dry are also essential.
Yogic Management for Hyperthermia
Yogic management plays a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being and can be particularly beneficial in managing hyperthermia. The combination of specific yogic practices and asanas (postures) helps regulate body temperature and supports the body’s natural cooling mechanisms.
Pranayama for Cooling
Sheetali Pranayama (Cooling Breath): This pranayama involves rolling the tongue and inhaling through the mouth. It cools the incoming air and helps reduce body temperature. Practice this in a well-ventilated space to maximize its benefits.
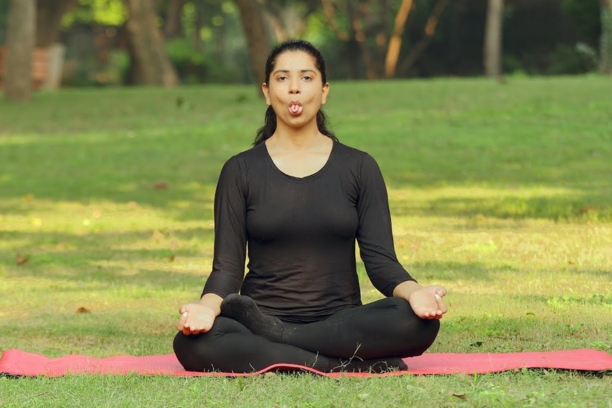

Sheetkari pranayama: Sheetkari pranayama is practiced by inhaling air through the sides of the mouth through closed teeth to reduce the increased body temperature in case of Hyperthermia
Cooling Yogasanas
Tadasana (Mountain Pose): This foundational asana promotes proper alignment and improves posture. It enhances blood circulation, which can be beneficial in managing hyperthermia.

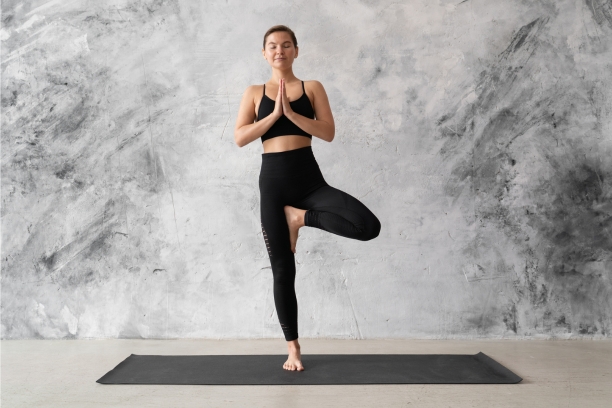
Vrikshasana (Tree Pose): This balancing pose helps improve concentration and mental clarity, which can be particularly helpful when dealing with hyperthermia-related discomfort.

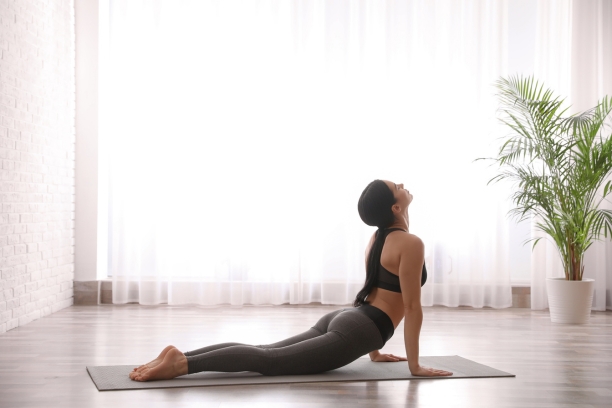
Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose): The cobra pose helps expand the chest, aiding in better breathing and promoting circulation.

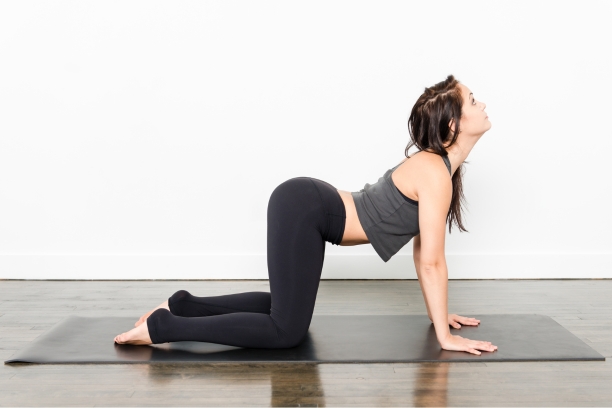
Cat-Cow Stretch: This gentle, flowing sequence of two poses improves spinal flexibility, warms up the body, and relieves stress.

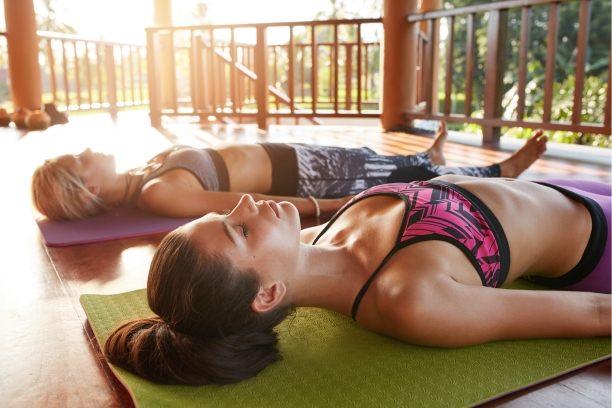
Savasana (Corpse Pose): Savasana is a relaxation pose that allows the body to cool down and recover after yoga practice.

Cooling Meditation
Meditation plays a significant role in calming the mind, reducing stress, and promoting mental clarity. Meditation techniques that focus on visualization and deep relaxation can help cool the mind and body.
Hydration Awareness
Yogic management emphasizes the importance of maintaining proper hydration through the consumption of clean water and hydrating foods. Staying hydrated is vital in regulating body temperature and avoiding heat-related illnesses.
Cooling Mantras
The recitation of certain mantras, such as the “Om Shanti” mantra, can have a calming and cooling effect on the mind and body.
Incorporating these yogic practices and asanas into your routine can complement other naturopathic treatments for hyperthermia. Practicing yoga mindfully and in a well-ventilated area is essential for safety and maximum benefit.
Yogic Management for Hypothermia
Yoga is a holistic practice that encompasses physical postures, breath control, and meditation. When it comes to hypothermia, certain yogic techniques can be particularly beneficial for restoring warmth to the body and promoting overall well-being. Here are some yogic management strategies for hypothermia:
- Surya Namaskar (Sun Salutation): This sequence of yoga postures provides a full-body warm-up, stimulating circulation and gently increasing body temperature.

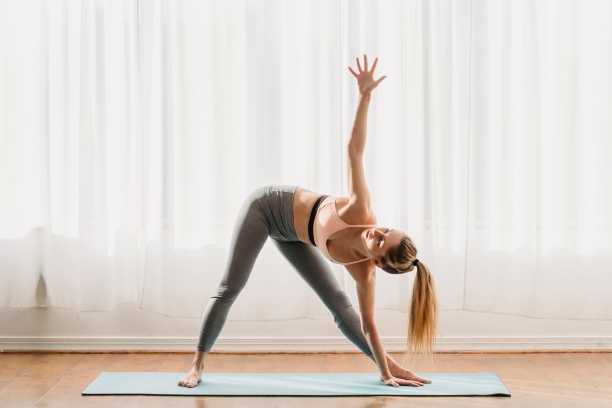
- Trikonasana (Triangle Pose): Trikonasana involves stretching and extending the body, increasing blood flow to the extremities and improving muscle tone.

- Matsyasana (Fish Pose): Matsyasana opens up the chest and helps improve lung function. Deep, full breaths can generate internal heat.
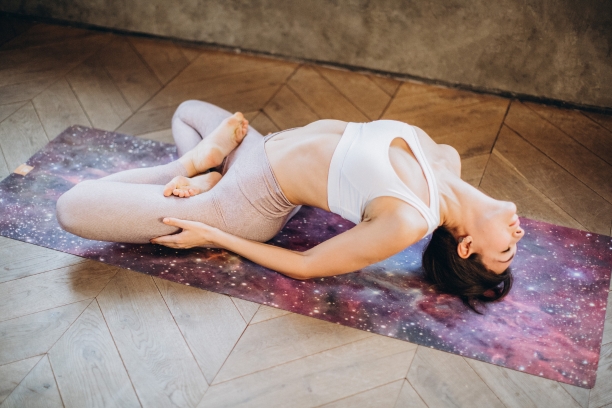

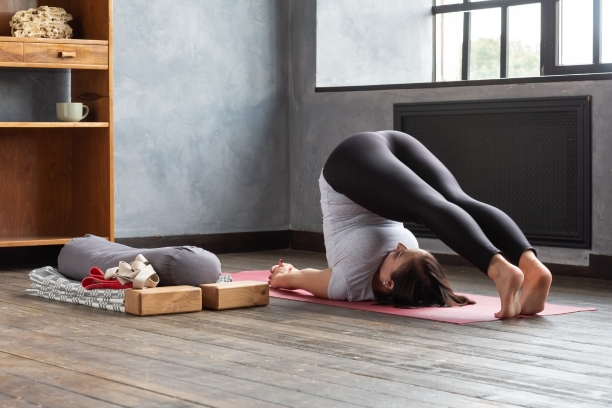
- Halasana (Plow Pose): Halasana can help stimulate the thyroid gland, which plays a significant role in regulating body temperature.

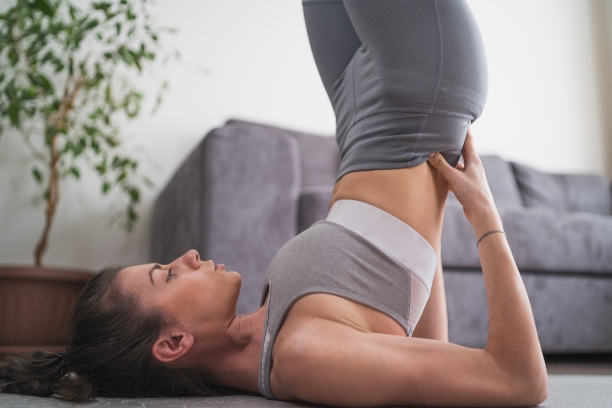
- Sarvangasana (Shoulder Stand): This pose can encourage circulation and improve overall body warmth.

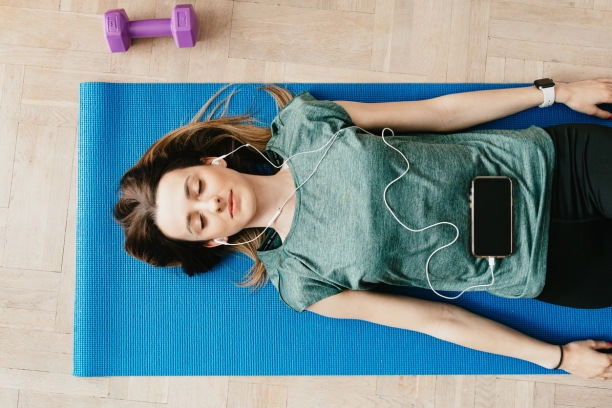
- Shavasana (Corpse Pose): Shavasana is a relaxation posture that can help the body recover and conserve energy.

- Bhastrika Pranayama (Bellows Breath): Bhastrika pranayama involves forceful inhalations and exhalations through the nose, generating internal heat and increasing oxygen supply to the body.

- Kapalbhati Pranayama (Skull Shining Breath): Kapalbhati pranayama is a dynamic breath control technique that stimulates circulation and generates internal warmth.

- Anulom Vilom Pranayama (Alternate Nostril Breathing): Anulom Vilom pranayama helps balance the body’s energy and enhances lung function.
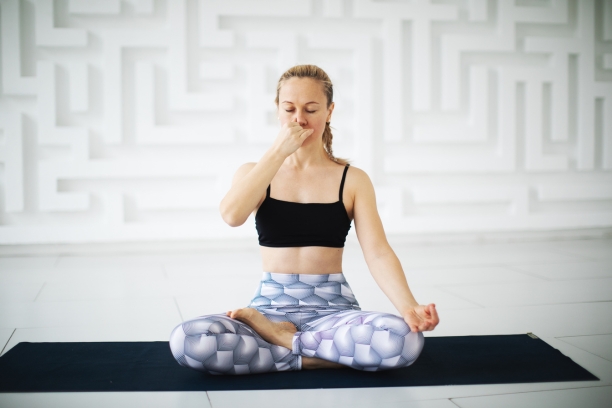

- Suryabhedi Pranayama: Suryabhedi pranayama is a yogic breathing exercise that aids in managing hypothermia by generating internal heat. This practice is performed by primarily breathing through the right nostril, associated with warming energy in yoga. Here’s a brief guide:

Conclusion
- The Holistic Approach to Temperature Management
- Embracing Naturopathic Wisdom for Optimal Well-Being
Hypothermia is a serious condition that demands immediate attention. Integrating naturopathic principles and practices alongside conventional treatments can provide holistic support for individuals at risk of or affected by hypothermia.