Introduction
Gestational diabetes is a temporary form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. It can lead to complications for both the mother and baby if not managed properly. While medical interventions are available, many women with gestational diabetes seek natural and holistic approaches to manage their condition. Naturopathy, with its focus on natural remedies and lifestyle modifications, offers valuable options for managing gestational diabetes. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore naturopathic treatments and therapies that can help pregnant women with gestational diabetes maintain healthy blood sugar levels and ensure a safe pregnancy.
Understanding Gestational Diabetes
Definition: Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy in women who did not have diabetes before conceiving.
Causes: The exact cause of GDM is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes during pregnancy.
Risk Factors: Some factors that increase the risk of developing GDM include:
- Obesity: Women with a higher body mass index (BMI) are more likely to develop GDM.
- Age: Women over the age of 25, especially those over 35, are at a higher risk.
- Family History: A family history of diabetes can increase the risk.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African American, Hispanic, Native American, and Asian American, are at higher risk.

Complications: Untreated or poorly managed gestational diabetes can lead to various complications, including:
- Macrosomia: The baby grows larger than normal, which can lead to birth injuries.
- Hypoglycemia: The baby may have low blood sugar at birth.
- Preeclampsia: A condition characterized by high blood pressure during pregnancy.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Women with GDM are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) develops during pregnancy and is characterized by high blood sugar levels. While the exact cause of GDM is not fully understood, several factors contribute to its development:
- Hormonal Changes: During pregnancy, the placenta produces hormones that can interfere with the way insulin works. This hormonal imbalance can lead to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t respond effectively to insulin.
- Insulin Resistance: As pregnancy progresses, the mother’s body may require up to three times more insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. When the body can’t produce enough insulin to meet this demand, blood sugar levels rise, leading to GDM.
- Genetic Predisposition: Women with a family history of diabetes are at a higher risk of developing GDM. Genetic factors can make some individuals more susceptible to insulin resistance.
- Obesity: Excess body weight, especially before pregnancy, is a significant risk factor for GDM. Obesity can increase insulin resistance, making it harder for the body to regulate blood sugar levels.

- Age: Women over the age of 25, especially those over 35, are at a higher risk of developing GDM. The risk increases with age as the body’s insulin sensitivity decreases.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, including African American, Hispanic, Native American, and Asian American, have a higher risk of GDM.
- Previous Gestational Diabetes: Women who had GDM during a previous pregnancy are more likely to develop it again in subsequent pregnancies.
Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes often doesn’t present with noticeable symptoms. It’s typically diagnosed through routine prenatal screening tests. However, some women may experience subtle signs that can indicate elevated blood sugar levels:

- Increased Thirst: Some women may notice an increase in thirst and may need to urinate more frequently.
- Fatigue: Elevated blood sugar levels can lead to fatigue and a feeling of being unwell.
- Increased Hunger: You may find yourself more hungry than usual, even after eating.
- Blurred Vision: Some women may experience blurred vision due to temporary changes in eye fluid caused by fluctuating blood sugar levels.
- Frequent Infections: High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections, particularly urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Yeast Infections: Women with GDM may be more prone to yeast infections, which can cause itching and discomfort in the genital area.
Naturopathic Approaches to Managing Gestational Diabetes
Managing gestational diabetes through naturopathy involves a holistic approach that addresses the physical, emotional, and nutritional aspects of a woman’s health during pregnancy. Here are various naturopathic treatments and therapies that can be beneficial:
- Dietary Modifications: Naturopathic doctors often emphasize dietary changes as a cornerstone of managing gestational diabetes. They may recommend a diet that’s rich in whole foods, low in refined carbohydrates, and balanced in macronutrients. This can help regulate blood sugar levels and ensure adequate nutrition for both mother and baby.

- Nutritional Supplements: Certain supplements, such as chromium, magnesium, and alpha-lipoic acid, may be recommended to support blood sugar regulation. These supplements can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of complications.

- Herbal Remedies: Some herbal remedies, like cinnamon and fenugreek, have been studied for their potential to lower blood sugar levels. However, it’s essential to use these under the guidance of a qualified naturopathic doctor or healthcare provider, as they can interact with medications or other treatments.

- Physical Activity: Regular exercise, tailored to the individual’s needs and pregnancy stage, can help improve insulin sensitivity and manage blood sugar levels. Naturopathic doctors may recommend safe and appropriate exercises, such as prenatal yoga or gentle walking.

- Stress Management: Stress can impact blood sugar levels. Naturopathic approaches often include stress reduction techniques like mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or biofeedback to help manage stress during pregnancy.

- Hydrotherapy: Hydrotherapy treatments, such as contrast baths or warm water soaks, may promote relaxation and improve circulation, potentially aiding in blood sugar regulation.
- Acupuncture and Acupressure: Traditional Chinese medicine techniques like acupuncture and acupressure can be used to support overall health and potentially help manage gestational diabetes symptoms.
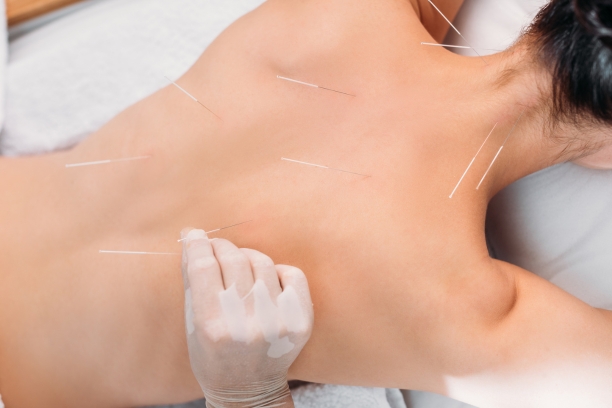
- Detoxification: Gentle detoxification methods may be recommended to support the body’s natural processes of eliminating waste and toxins, which can contribute to overall health and metabolic function.

- Education and Lifestyle Counseling: Naturopathic doctors often provide education and lifestyle counseling to help women with gestational diabetes make informed choices about their health. This may include guidance on meal planning, stress reduction, and self-care practices.
- Collaboration with Conventional Care: Naturopathic doctors typically work in collaboration with obstetricians and other healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive care for the mother and baby. This includes monitoring blood sugar levels, adjusting treatment plans as needed, and addressing any potential complications.
Yogic management for gestational diabetes can be a valuable addition to conventional medical care. Yoga offers a holistic approach to health that includes physical postures, breathing exercises, meditation, and relaxation techniques. Here’s how yogic management can benefit women with gestational diabetes:
- Stress Reduction: Pregnancy, coupled with a gestational diabetes diagnosis, can lead to increased stress levels. Yoga’s emphasis on deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness can help reduce stress hormones like cortisol, which can affect blood sugar levels.

- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Certain yoga poses, such as forward bends and twists, can stimulate the pancreas and enhance insulin sensitivity. These postures can help the body utilize glucose more effectively, potentially leading to better blood sugar control.

- Physical Fitness: Gentle yoga postures and stretches can improve overall fitness and flexibility. This can be especially beneficial during pregnancy, as it helps maintain strength and reduces discomfort associated with the changing body.

- Blood Circulation: Yoga poses and movements encourage blood circulation, which is essential for the well-being of both the mother and baby. Improved circulation can support the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to tissues and organs, including the placenta.
- Stabilized Blood Sugar: Regular practice of yoga, combined with mindfulness around eating, can help stabilize blood sugar levels. This can prevent spikes and crashes, creating a more even and controlled blood sugar profile.
- Pelvic Floor Strength: Specific yoga exercises, like Kegels and certain asanas, can strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. This is important for pregnant women as it can help with bladder control and support the growing uterus.
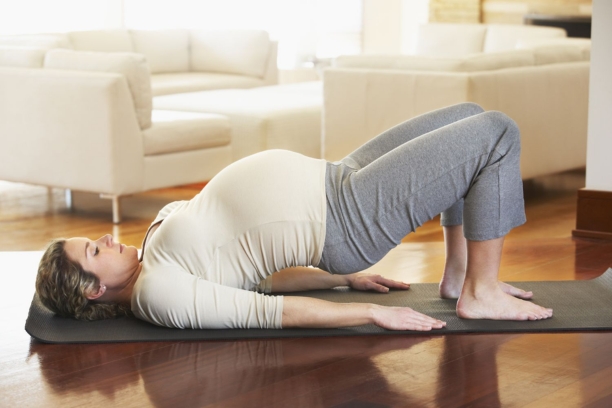

- Emotional Balance: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to mood swings and emotional imbalances. Yoga and meditation can help women connect with their emotions and maintain emotional well-being during this transformative period.
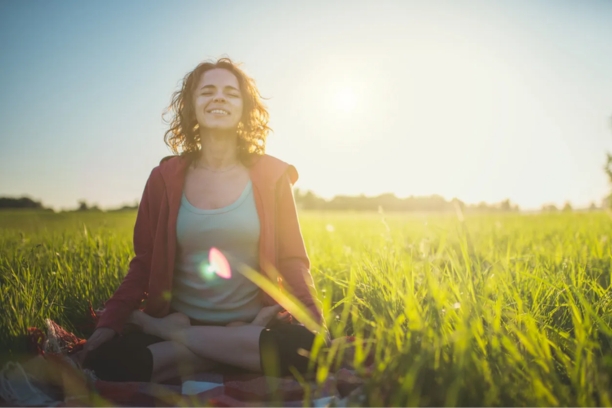

- Preparation for Labor: Prenatal yoga often includes poses and breathing techniques that prepare the body for labor and childbirth. These exercises can enhance endurance and provide relaxation methods for labor pain management.

- Community Support: Participating in prenatal yoga classes can create a supportive community of expectant mothers. Sharing experiences and building connections with others going through similar situations can be emotionally uplifting.
- Postpartum Recovery: Yoga can be a valuable tool for postpartum recovery, helping women regain strength, flexibility, and emotional balance after childbirth.

It’s essential to engage in yoga practices that are specifically designed for pregnancy, as they consider the safety and comfort of expectant mothers. Always consult with a qualified yoga instructor who specializes in prenatal yoga to ensure you’re practicing poses and exercises that are appropriate for your stage of pregnancy and medical condition.
Conclusion
Gestational diabetes can be effectively managed through naturopathic approaches that emphasize holistic well-being. It’s essential for pregnant women with GDM to work closely with a qualified naturopathic doctor to create a personalized treatment plan that addresses their unique needs.It’s crucial for women with gestational diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team, which may include naturopathic doctors, to develop an individualized care plan.