Principles of Manipulative Therapy
- Basis in Anatomy and Physiology
- Mechanisms of Action
- Alignment and Balance
Types of Manipulative Therapy
- Chiropractic Manipulation
- Techniques and Adjustments
- Conditions Treated
- Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment (OMT)
- Philosophical Foundation
- Techniques Used
- Physical Therapy Manipulation
- Role in Rehabilitation
- Evidence-Based Practices
- Massage Therapy
- Soft Tissue Manipulation
- Therapeutic Benefits
Conditions Addressed by Manipulative Therapy
- Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Back Pain
- Neck Pain
- Joint Issues
- Headaches and Migraines
- Efficacy of Manipulative Therapy
- Postural and Alignment Issues
- Role in Correcting Alignment
- Inflammatory Conditions
- Arthritis and Manipulative Therapy
1. Understanding Manipulative Therapy
Defining Manipulative Therapy
Manipulative therapy, also known as manual therapy, encompasses a range of hands-on techniques aimed at diagnosing, treating, and preventing musculoskeletal conditions. Practitioners utilize their hands to assess and treat joints, muscles, and soft tissues, aiming to restore optimal function and alleviate pain.

Historical Roots
The roots of manipulative therapy trace back to ancient healing practices. Over centuries, different cultures have contributed to the evolution of these techniques, with notable influences from traditional Chinese medicine, Greek medicine, and various manual healing traditions.
2. Principles of Manipulative Therapy
Holistic Assessment
One key principle of manipulative therapy is a holistic assessment of the patient. Practitioners consider not only the specific area of discomfort but also the interconnectedness of the musculoskeletal system. This approach allows for a comprehensive understanding of the underlying issues.
Hands-On Techniques
The hallmark of manipulative therapy is its hands-on nature. Practitioners employ a variety of techniques, including joint mobilization, soft tissue manipulation, and muscle energy techniques. The goal is to enhance joint mobility, release muscle tension, and improve overall function.
3. Types of Manipulative Therapy
Chiropractic Manipulation: Aligning the Spine
Key Principles
Chiropractic Manipulation, often synonymous with spinal adjustments, revolves around the principles of restoring proper alignment to the spine. Chiropractors employ controlled and precise force to targeted joints, primarily in the spine, aiming to alleviate pain, enhance mobility, and optimize overall musculoskeletal function.
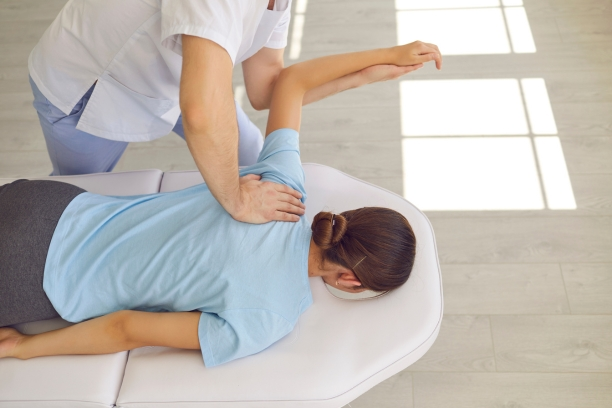

Techniques
- Spinal Adjustments: The hallmark of chiropractic care, spinal adjustments involve gentle but purposeful movements to realign vertebrae, addressing issues such as subluxations and promoting optimal nerve function.
- Joint Mobilization: Beyond the spine, chiropractors may utilize joint mobilization techniques to address misalignments in peripheral joints, fostering a comprehensive approach to musculoskeletal health.
Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment (OMT)
Key Principles
Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment (OMT) is rooted in the philosophy that the body possesses inherent self-healing mechanisms. Osteopathic physicians leverage OMT as a comprehensive approach, addressing structural imbalances and promoting optimal function throughout the body.
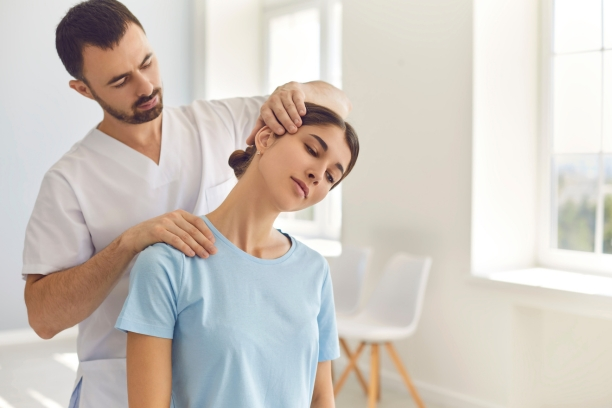

Techniques
- Soft Tissue Techniques: OMT encompasses a range of soft tissue techniques, including myofascial release and muscle energy techniques, designed to address tension and imbalances in muscles and connective tissues.
- Articulatory Techniques: Osteopathic physicians employ gentle joint mobilization and articulation techniques to enhance joint function, promote circulation, and restore the body’s natural rhythm.
Physical Therapy Manipulation
Physical Therapy Manipulation integrates hands-on techniques into the broader spectrum of physical therapy. Physical therapists tailor their approach based on individual needs, addressing musculoskeletal issues through targeted interventions.
Techniques
- Joint Mobilization: Similar to chiropractic care, physical therapists may use joint mobilization to improve joint range of motion and alleviate stiffness.
- Soft Tissue Massage: Soft tissue manipulation, including massage therapy, is often incorporated to reduce muscle tension, promote relaxation, and enhance overall tissue health.
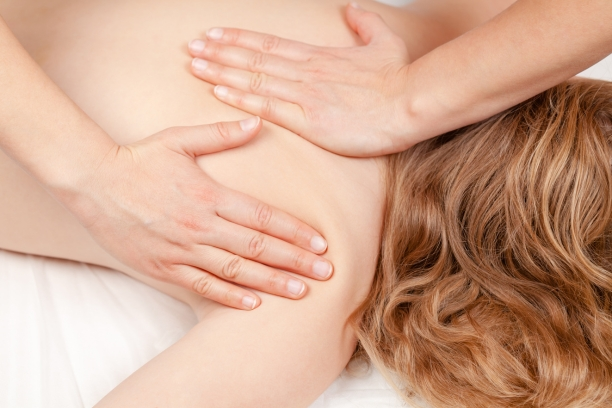
Massage Therapy: Therapeutic Touch
Key Principles
Massage Therapy transcends the realms of relaxation, embracing therapeutic principles that contribute to musculoskeletal well-being. It involves the manual manipulation of soft tissues, aiming to reduce tension, improve circulation, and foster a sense of overall physical and mental balance.
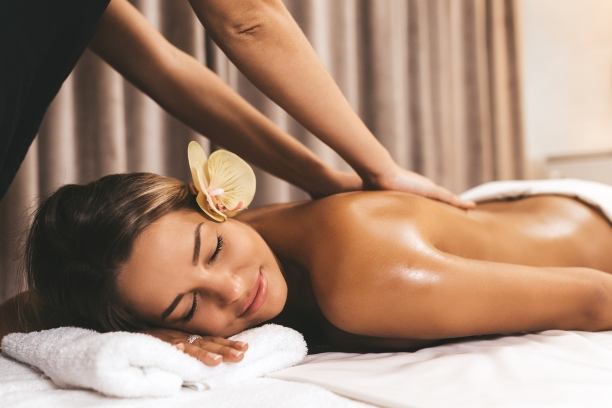

Techniques
- Swedish Massage: A foundational technique, Swedish massage involves long, flowing strokes, kneading, and circular movements to promote relaxation and relieve muscle tension.
- Deep Tissue Massage: Targeting deeper layers of muscles, deep tissue massage addresses chronic tension and may be particularly beneficial for individuals with specific musculoskeletal concerns.
Conditions Addressed by Manipulative Therapy
Musculoskeletal Pain
Manipulative therapy is widely utilized for the management of musculoskeletal pain, including back pain, neck pain, and joint pain. The hands-on approach helps alleviate discomfort and improve range of motion.
Sports Injuries
Athletes often benefit from manipulative therapy to address sports-related injuries. Techniques such as joint mobilization and soft tissue manipulation can contribute to the rehabilitation process and prevent future injuries.
Postural Issues
Poor posture can contribute to various musculoskeletal issues. Manipulative therapy helps address postural imbalances, promoting optimal alignment and reducing the risk of associated problems.
5. Benefits and Considerations
Pain Relief
One of the primary benefits of manipulative therapy is pain relief. By addressing structural issues and improving joint function, individuals often experience a reduction in pain and discomfort.
Improved Mobility
Manipulative therapy aims to enhance joint mobility and flexibility. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions causing stiffness or restricted movement.
Individualized Approach
Practitioners tailor manipulative therapy to the individual’s unique needs. The treatment plan is often personalized based on the specific condition, overall health, and patient preferences.
New Blog: Naturopathy for Improved Sleep Quality